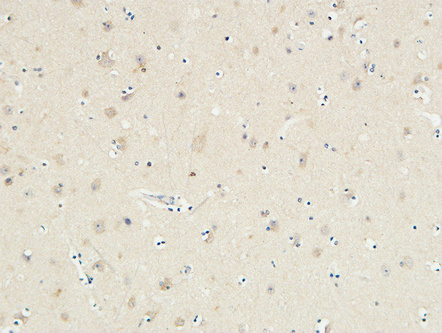
KiSS-1R Polyclonal Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

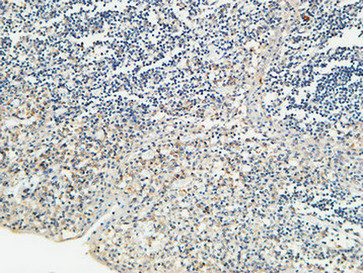
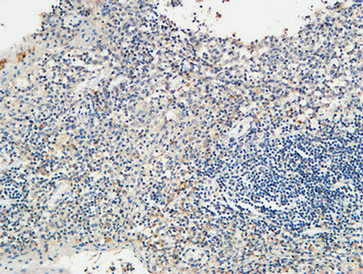
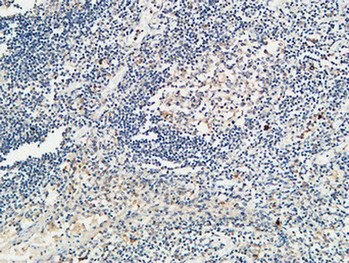
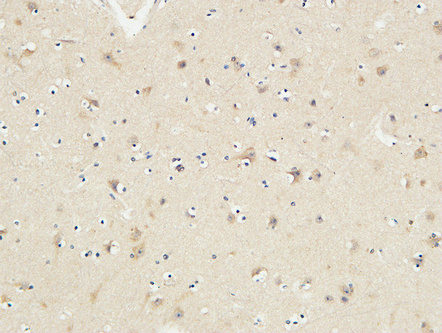
Application
| IF |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q969F8 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Calculated MW | 42586 Da |
| Gene ID | 84634 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | KISS1R; AXOR12; GPR54; KiSS-1 receptor; KiSS-1R; G-protein coupled receptor 54; G-protein coupled receptor OT7T175; hOT7T175; Hypogonadotropin-1; Kisspeptins receptor; Metastin receptor |
| Dilution | IF~~Immunofluorescence: 1/200 - 1/1000. ELISA: 1/5000. Not yet tested in other applications. |
| Format | Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.09% (W/V) sodium azide. |
| Storage Conditions | -20℃ |
| Name | KISS1R |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | AXOR12 {ECO:0000303|PubMed:11387329}, GP |
| Function | Receptor for kisspeptins (kisspeptin-10, kisspeptin-13, kisspeptin-14 and metastin/kisspeptin-54) (PubMed:11457843, PubMed:11527393, PubMed:15020672, PubMed:15596153). The hypothalamic KISS1/KISS1R signaling system plays a central role in the regulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal reproductive axis by modulating the secretion of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) from GnRH neurons (PubMed:12944565, PubMed:14573733, PubMed:15598687, PubMed:17164310, PubMed:18272894). In these neurons, kisspeptin binding to its receptor activates G(q)-dependent signaling, leading to phospholipase C (PLC) activation, and hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) (PubMed:14573733, PubMed:15598687, PubMed:39151001). The subsequent rise in intracellular calcium levels results in the inhibition of inward rectifier potassium channels and activation of TRPC-like cation channels, leading to GnRH neurons depolarization and stimulation (By similarity). In addition to this pathway, kisspeptin also triggers G(q)-independent signaling via beta-arrestin, leading to MAPK cascade activation and ERK1/ERK2 phosphorylation (PubMed:25147978). Furthermore, activation of KISS1R by kisspeptin-10 recruits phosphatase DUSP18 and SRC to the KISS1R C-terminus through a G(q)-dependent signaling pathway, leading to DUSP18-mediated dephosphorylation of SRC (PubMed:38346942). In bone tissue, this results in down-regulation of osteoclast differentiation and activity, and consequently suppression of bone resorption (By similarity). KISS1R is also involved in the regulation of other processes, including cell proliferation and cell migration (PubMed:11457843, PubMed:11527393, PubMed:15020672, PubMed:15596153, PubMed:38512807). |
| Cellular Location | Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein |
| Tissue Location | Expressed in the pancreas, placenta and spinal cord, with lower-level of expression in peripheral blood leukocytes, kidney, lung, fetal liver, stomach, small intestine, testes, spleen, thymus, adrenal glands and lymph nodes. In the adult brain, expressed in the superior frontal gyrus, putamen, caudate nucleus, cingulate gyrus, nucleus accumbens, hippocampus, pons and amygdala, as well as the hypothalamus and pituitary. Expression levels are higher in early (7-9 weeks) than term placentas. Expression levels were increased in both early placentas and molar pregnancies and were reduced in choriocarcinoma cells. Expressed at higher levels in first trimester trophoblasts than at term of gestation. Also found in the extravillous trophoblast suggesting endocrine/paracrine activation mechanism |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
Receptor for metastin (kisspeptin-54 or kp-54), a C- terminally amidated peptide of KiSS1. KiSS1 is a metastasis suppressor protein that suppresses metastases in malignant melanomas and in some breast carcinomas without affecting tumorigenicity. The metastasis suppressor properties may be mediated in part by cell cycle arrest and induction of apoptosis in malignant cells. The receptor is essential for normal gonadotropin-released hormone physiology and for puberty. The hypothalamic KiSS1/KISS1R system is a pivotal factor in central regulation of the gonadotropic axis at puberty and in adulthood. The receptor is also probably involved in the regulation and fine- tuning of trophoblast invasion generated by the trophoblast itself. Analysis of the transduction pathways activated by the receptor identifies coupling to phospholipase C and intracellular calcium release through pertussis toxin-insensitive G(q) proteins.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.




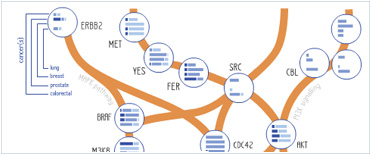







 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.